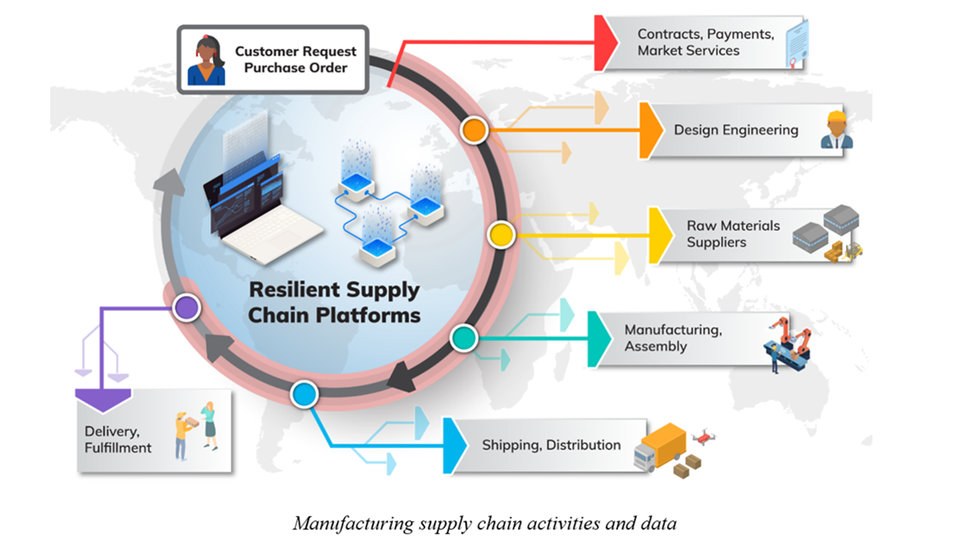
In today’s fast-paced business environment, supply chain managers are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and boost overall efficiency. The integration of AI into supply chain management can offer substantial benefits, including improved accuracy in demand forecasting, enhanced procurement processes, optimization of warehouse operations, predictive maintenance, and robust risk management. Here’s how supply chain managers can practically apply AI in their daily activities:
Adopt AI-Enhanced Demand Forecasting
Traditional demand forecasting methods, while useful, often fall short in predicting accurate future demands. AI steps in to fill this gap by analyzing vast amounts of historical sales data, market trends, and external variables such as weather conditions. By leveraging AI algorithms, supply chain managers can produce more precise demand forecasts, enabling optimized inventory management and more efficient production scheduling.
Streamline Procurement with AI Assistance
AI can revolutionize procurement by automating routine tasks through the use of AI-powered chatbots. These bots can handle supplier inquiries, process basic order confirmations, and manage delivery schedules, freeing human workers to concentrate on strategic procurement decisions. This not only saves time but also increases the procurement process’s efficiency and accuracy.
Enhance Warehouse Efficiency with AI
AI technologies offer significant improvements in warehouse management, from optimizing the layout for better space utilization to automating picking and packing processes with robots. AI-driven route planning also ensures that warehouse operations are more efficient, reducing manual labor errors and enhancing throughput.
Implement Predictive Maintenance through AI
By monitoring equipment and machinery with AI systems, supply chain managers can predict and prevent potential failures before they disrupt operations. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces the risk of costly production stoppages, and ensures a smoother production flow.
Strengthen Supply Chain Resilience with AI-Powered Risk Management
AI algorithms are adept at analyzing real-time data on potential supply chain threats, such as adverse weather conditions or geopolitical tensions. By leveraging AI for risk management, supply chain managers can develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks, ensuring that they can quickly respond to unexpected challenges.
Incorporating AI into daily supply chain management practices offers a pathway to not only improve operational efficiency but also to achieve cost savings and bolster supply chain resilience. As supply chain managers embrace these practical AI applications, they unlock the potential to navigate the complexities of modern supply chains more effectively.